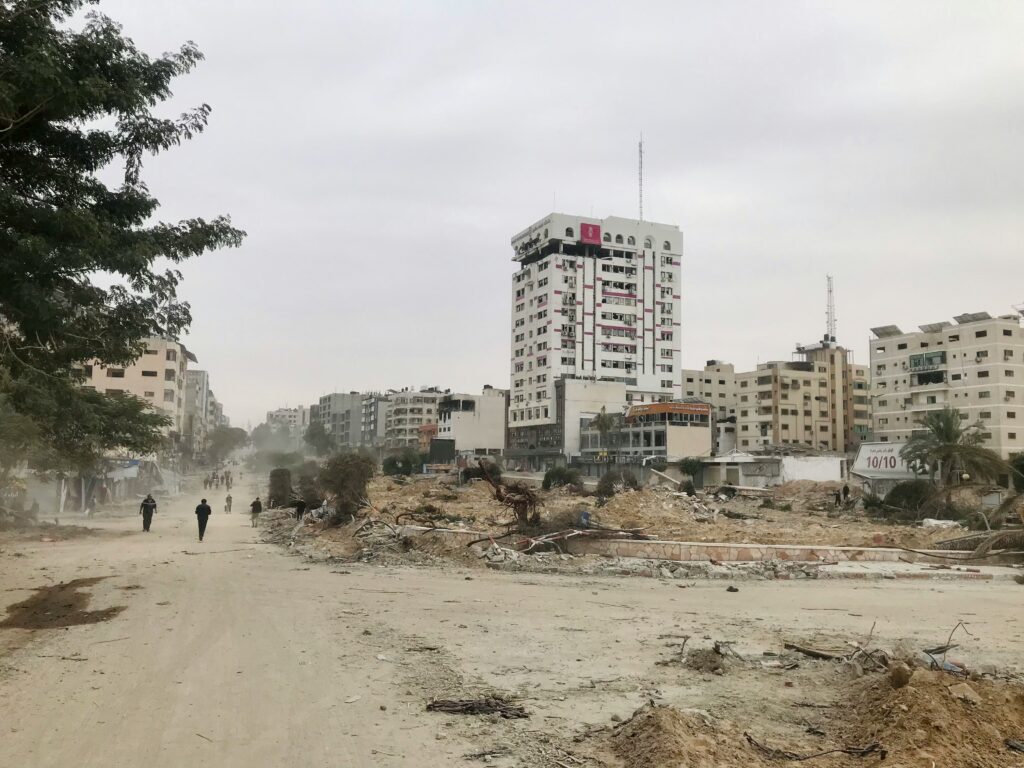
In recent years, there have been increasing global consumer boycotts against Starbucks, stemming from allegations that the company supports the Israeli political system and is indirectly involved in expansionist policies and conflicts with the Palestinians, including the situation in the Gaza Strip.
The Beginning of the Boycotts
The boycotts began when activists and human rights organizations claimed that Starbucks openly supported Israel. These allegations were further fueled by rumors and misinformation about donations from Howard Schultz, the former CEO of Starbucks, to pro-Israeli organizations. Although Starbucks has repeatedly stated that the company has no political agenda and provides no financial support to Israeli or other political entities, public opinion remained divided. The core of these allegations lies in the complex and often polarized opinions about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, where any sign of support for Israel is seen by some as an endorsement of controversial policies.
Global Spread of the Boycotts
The boycotts against Starbucks started small but quickly spread across various countries. From the United States to Europe, and from the Middle East to Asia, consumer organizations and activists called for avoiding Starbucks products. These boycotts were often supported by large-scale social media campaigns, where activists urged their followers to seek alternatives for their daily coffee. A significant moment in the spread of these boycotts was the establishment of the BDS movement (Boycott, Divestment, Sanctions), which aims to exert economic and political pressure on Israel through global boycotts.
Methods of Boycotting
The methods by which consumers boycott Starbucks vary. Some choose to simply stop buying Starbucks products, while others organize active campaigns to raise awareness. Petitions, protests in front of Starbucks stores, and the use of hashtags such as #BoycottStarbucks on social media are some of the tactics used to pressure the company. In some cases, activists have even created apps and websites recommending alternatives to Starbucks, promoting local coffee shops that have no ties to controversial political issues.
Prominent Figures and Activists Involved in the Consumer Boycotts of Starbucks
Various well-known figures and activists have spoken out in favor of boycotting Starbucks. One of the prominent figures is Roger Waters, the former bassist and singer of Pink Floyd, who is a leading supporter of the BDS movement. Waters has repeatedly called for a cultural and economic boycott of Israeli products and companies involved in Israeli politics.

Another well-known activist is Alice Walker, the Pulitzer Prize-winning author of “The Color Purple”. Walker has used her platform to raise awareness about the situation in Palestine and the boycott of companies like Starbucks that are seen as supportive of Israel.
Additionally, Irish musician Sinead O’Connor has publicly expressed her support for the boycott. O’Connor, known for her political and social activism, has stated that she does not want her money to indirectly support Israeli politics.
Journalist and activist Naomi Klein, known for her books “No Logo” and “The Shock Doctrine”, has also spoken out in favor of boycotting Starbucks. Klein is a vocal critic of globalization and the influence of multinationals on politics and society, and sees the boycott as a means to hold companies accountable for their ethical and political choices.

Reasons for the Boycott
The reasons behind the boycott are diverse but often relate to the perception that Starbucks has a pro-Israeli stance. Activists point out that by boycotting Starbucks, they express their discontent with Israeli expansionist policies and the treatment of Palestinians. For some, boycotting Starbucks is a way to show solidarity with the Palestinian cause and take a stand against injustice. Additionally, the broader context of global political solidarity plays a role, where consumers in different countries unite to exert collective pressure on multinationals suspected of involvement in political or ethical misconduct.
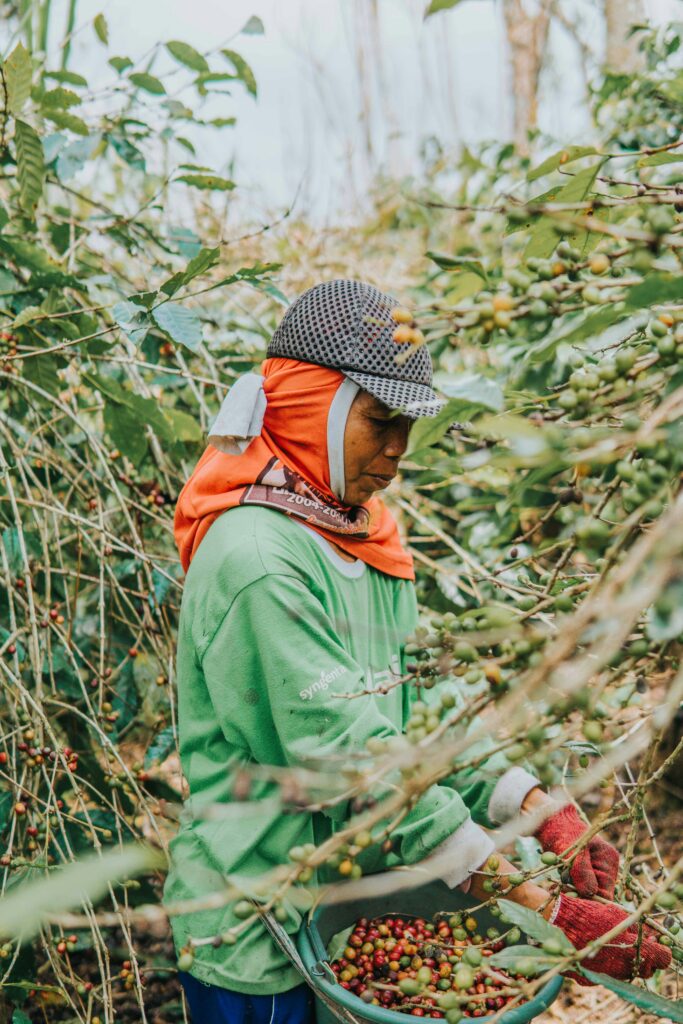
Criticism of Starbucks: Working Conditions on Coffee Plantations
In addition to the recent boycotts, Starbucks has faced criticism in the past for the working conditions on coffee plantations from which the company sources its beans. Activists and human rights organizations have reported low wages, poor working conditions, and child labor on some plantations supplying coffee to Starbucks. These allegations have led to a broader discussion about the ethical responsibility of multinationals in their supply chains.
Starbucks has taken steps to address this criticism through initiatives such as the C.A.F.E. Practices program (Coffee and Farmer Equity Practices), established to ensure that coffee beans are sourced ethically and sustainably. This program includes guidelines for fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmental management, and collaborates with certification organizations such as Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance. Despite these efforts, some critics remain skeptical about the effectiveness and transparency of these measures.
Consequences for Starbucks
The boycotts and ongoing criticism of Starbucks’ ethical practices have had significant consequences for the company. Not only does the company face declining sales in certain regions, but it also suffers from reputational damage. In an attempt to counter the negative publicity, Starbucks has issued multiple statements emphasizing that the company supports no political agenda. Additionally, Starbucks is investing more in corporate social responsibility and initiatives aimed at supporting local communities. This includes promoting ethical sourcing practices for coffee beans, supporting education and healthcare projects in coffee-producing countries, and enhancing environmentally friendly business practices.
In terms of numbers, Starbucks reported a 5-10% decline in sales in some markets following calls for boycotts. This decline was particularly felt in the Middle East and some European countries. Additionally, there has been a significant increase in negative sentiment on social media, with a 30% rise in negative mentions since the start of the boycott campaigns. The company has also faced an increased number of protests and demonstrations in front of its stores, leading to disruptions and sometimes temporary closures of stores.
Conclusion
The boycotts of Starbucks demonstrate how consumer activism can impact a large corporation. Although the long-term effects of these boycotts remain to be seen, it is clear that companies in a globalized world are increasingly facing pressure from consumers demanding higher ethical standards. For Starbucks, it remains a challenge to regain the trust of its customers and demonstrate that it is a neutral, inclusive, and ethically responsible enterprise. It is a continuous process of adaptation and dialogue, where the company must remain open to feedback and be willing to take concrete steps to meet the expectations of an increasingly critical consumer base.